Small companies are finding themselves at crossroad when deciding whether they should go for IT solution specific for each function or a integrated solution.
Small companies are finding themselves at crossroad when deciding whether they should go for or stay with small IT solution very specific to their most painful area or go for integrated solution that can meet the short term solution to reduce pain areas but also help them in meeting challenges that are likely to appear in their path to grow and scale operations. We are taking calibration labs as a case study for this paper but this dilemma is leaving number of leaders confused thus I hope this reading will be helpful to the other small companies leaderships as well.
A case study taking Calibration laboratories
As I was recently talking to a small calibration lab based in eastern part of India and the point was prominently and frankly discussed between two of us. The COO mentioned that, even though the idea of one application appeals to him, but they already have many systems in their lab and he is not sure whether any integrated application will be of any benefit to their organization.
Though there are many subjective reasons why one application looks more attractive in comparison to many small applications but I knew without quantitative assessment, it will be difficult to make any convincing argument in favor of integrated solution. So, I started working on collating various factors that could contribute to quantification of benefits and conclusively establish the argument in favor or against one integrated application.
Calibration Lab operations in nutshell: It is important to understand operations before we go further to understand his dilemma
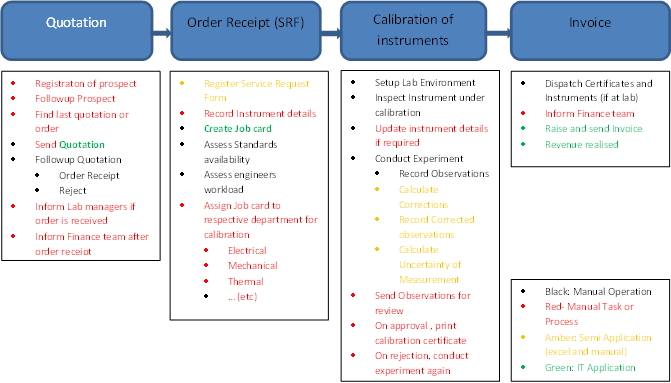
Highlights of the calibration operations :
Quotation stage:
- Assignment to sales person is subjective and manual
- Records and statistics are maintained partly or by individuals for the sake of calculating bonus or sales incentive
- Loss of last proposal (rejected ones ) when it was rejected on the basis of cost
- Determine last quoted price from order and invoice is tedious task
- Information to Lab Manager and Finance team is manual
Order receipts stage:
- Register SRF is manual exercise
- Registration of UUC is manual exercise and repeats itself everytime the instrument is received for calibration
- Creation of Job card is through IT application but limited to printing Job card
- Send the paper copy of Job card to each department is manual
- Assessment of workload and standard reference instruments is manual and many time received after coordination with the lab managers
Calibration stage:
- This is mostly manual activity except for calculations part (that are semi-automated with the help of numerous spreadsheets (for each instrument class, ie one for Mass, volume, other for surface plate)
- Correction calculations and observations are also sourced from software that accompanied hardware (ie standard instrument provider)
- Observations are recorded on paper invariably whether sourced from machine or people
- Uncertainty value are produced with the help of semi automated spreadsheets
- Certificate printing is mostly manual activity, published by a separate department mostly called reporting section
Invoicing stage:
- Information to invoicing team wrt calibration completed is manual and depends highly on coordination between Lab managers and Finance team
- Certificates are routed through invoicing team to plug any leakage
Though for all practical purposes, the above machinery and system of flow is working since many years, there are some potential pitfalls at many points and drop of ball by departments during the lifecycles many a times. But if we look deeper there are many activities that can result in reducing the cost. Most common mistake we do in assessing feasibility of software is not considering the benefit of automating processes which is clearly evident from the landscape earlier. Following class of factors are considered
- Monetary cost & Benefits
- Cost of Time or Efficiency advantage
- Subjective factors that cannot be assessed
Following table summarise the factors that requires to be considered for apple to apple comparison, better to cumulate the cost over a period of two to three years as the cost of new application may be higher in first year but may provide good return in following years. Assumption: We are assuming core single solution on software as service based hosted solution, this option has significantly reduced cost of ERP solutions deployment for end user enterprises.
1 Integrated application;Class A
| Sr.No. | Factor Narrative | Multiple Disparate IT Solutions | Single core solution (or ERP) | ||||||
| A.1 | Cumulative Cost of managing Software | Operational cost of small applications (license/AMC cost) | No license or AMC cost, cost is part of in per month usage cost | ||||||
| A.2 | Cost of maintaining hardware and other IT assets where software are hosted | (AMC/Repair/Backup cost) | Zero, as cost is part of per month usage cost | ||||||
| A.3 | Paper cost (operations that are still being done on paper and by people), cost of paper, its safe keeping and people to be included in the cost. | Cost of printed stationary consumed per year | Publish the document in software thus print only if required | ||||||
| A.4 | Cost of operations (report sections) | Cost of recording data and publishing certificates | Engineers can publish report themselves thus making report section redundant | ||||||
| A.5 | Cost of manpower coordinating between various functions within the enterprise | Cost of coordinator | Processes automated in the application thus coordination is automatic | ||||||
| Class B | Time | ||||||||
| B.1 | Access to Past data | Time spent in record room to unearth old archived records | In a matter of few clicks | ||||||
| B.2 | Lead time to act or react | Manual coordination thus lead time is +ve may depend on size and spread of organization | Information is very much real time | ||||||
| B.3 | Resource Productivity and workload management | Uneven or unbalanced workload at many times amongst engineers also amongst different labs | User can balance the workload as dashboard highlights task on everyone tray | ||||||
| B.4 | Timely engagement with customer and retention or attrition rate of customer | Number of times customers lost due to poor response or some other competitor engaged with customer earlier then you | Application post a reminder on sales representative mail and calendar next scheduled date of engagement | ||||||
| Class C | Qualitative factors | ||||||||
| C.1 | Improvement in quality of work delivered | Clerical and typo mistakes get released sometimes (pl specify on average per year) | All data standardized , clerical and typo errors removed | ||||||
| C.2 | Improvement in customer satisfaction for delivering consistent Excellent delivery | Satisfaction is derived from quality delivered | Assured quality | ||||||
| C.3 | Employee satisfaction, are employees being assessed on quantitative measures (number of instrument calibrated, number of sales made) | Lack of statistics wrt work delivered by employees often leads to subjective and unfair appraisal | Statistics is handy at any point of time and could be used as basis for appraisal. | ||||||
| C.4 | Information in hand | Not always, information archival is heavy job and often requires number of days | In hand at any point of day for any customer or product class | ||||||
| C.5 | Data loss or theft | New competitors started by past employees of the organization, who took valuable data on spreadsheets alongwith them | Data is managed within application, Information could be accessed only if authorized and exported in meaningful spreadsheet by authorized person only | ||||||
I will be thankful to readers for their comments and feedback on any factor that I might have missed to mention.